Baselines and Tolerances
Baselines are used to signify the expected or designed duration each motion will experience. Tolerances are used to denote how much variation from these baselines there can be before the motion is flagged. Motions will be flagged as "Watch" – the cycle duration exceeds the "NTol" value – or they will be flagged as "Warning" – the cycle exceeds the "Tol" value – which will display these motions on the "Hotspots" screen and is also used for reporting purposes.
There are 3 generally recommended – but not fully inclusive – methods of baseline and tolerance selection:
Choose a baseline value slightly above the normally expected cycle duration with tighter tolerance values.
Useful for setting standard tolerance values for common pieces of tooling.
Generally, tight variance cycles where a small overage denotes an immediate issue.
Choose a baseline value of an average expected cycle duration with wider tolerance values.
A more variable normal cycle duration useful for tracking cycles that exceed normally expected variance.
Generally, tight variance cycle where a larger overage is allowed.
Choose a baseline value as a hard limit with zero values for tolerances.
CycleTime group where an overage constitutes a machine over cycle condition.
Operator motions where a maximum time is given and any overage is considered an over cycle condition.
An agreed-upon maximum limit for a common piece of tooling is used to track tooling degradation for predictive maintenance purposes.
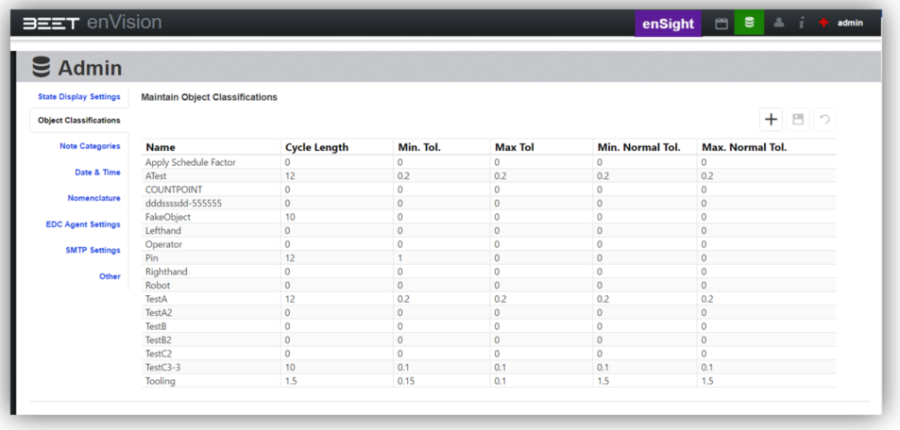
Object Classifications
Object Classifications are used to label common types of objects for easier usage for reporting purposes. By creating and assigning classifications to individual Group motions for each Asset, these objects can quickly be sorted and combined for reporting and data analysis. Commonly used classifications are Operator, Tooling, Robot, and Joining. These classifications are fully user-definable, and any group may be assigned multiple classifications.
Smart notes
Notes are used to add descriptions to a given cycle. Note categories and subcategories can be created or modified in the admin area of ENVISION. When a note is created on a given cycle, any previously created note category can be assigned to this note, and these notes can then be sorted and summarized based on their category. Notes are very useful for describing reasons and conditions for abnormal cycles; these notes remain persistent and are available to all users. See Note Categories.
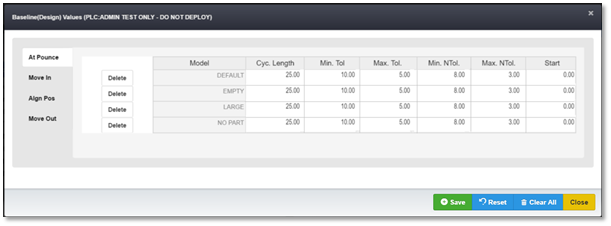
Baseline Values
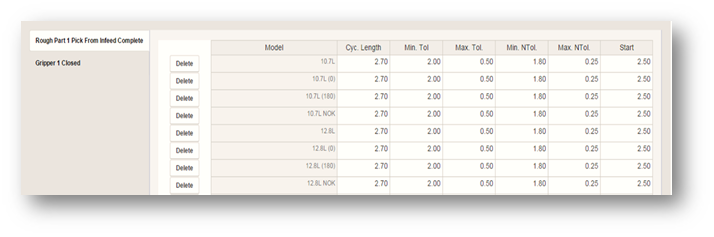
When the Baseline Values button is selected, the following window pops up. It is here where the data is entered for baseline (Cycle Time) and tolerances for the models that were created previously. This is the data that the Envision application uses to create the graphical representation of the cycles. For this reason, the MODEL Asset tag is of critical importance. Envision needs a value for the MODEL Asset tag or it will not know how to "draw" the cycle.
Every Group of the Asset will have a similar window that pops up when the Group object is highlighted and the Baseline Values button is clicked. For Group objects with 2 or more OP's, each OP will need values entered individually as required.
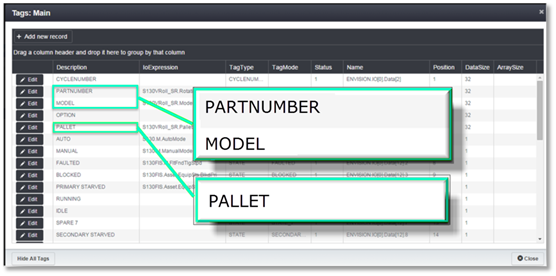
There were additional Asset Tags that appeared when the Show All Tags button was clicked. These tags can be used to display additional information for each cycle.
The CYCLENUMBER tag does not need an IoExpression and will be ignored if one is entered. This tag is automatically updated by the Envision PLC driver logic. The tag is displayed for informational purposes only.
The PARTNUMBER tag can be used to store a part tracking value such as a sequence number or rotation number if the process utilizes some sort of part monitoring. This is optional. If no IoExpression is entered, then Envision will display a zero.
The OPTION tag is currently not used by the Envision application for any display or calculation purposes. It is for future use. A value can be entered for the IoExpression but it will be ignored by the application.
The PALLET tag is fairly self-explanatory. It can be used to store part conveyance data such as a conveyor carrier I.D. number or a roller bed pallet I.D. This is optional. If no IoExpression is entered, then Envision will display a zero.
To edit model baselines and tolerances, go to any group object, then click the baseline tab at the top of the window. CycleTime baseline values will determine when the Asset starts and stops all other baselines will only affect Groups.
Baseline tables will differ from one another in terms of how many models each asset has, and how many OPs each group has. The values inputted in each cell will depend on how each model tied to the asset is intended to function.
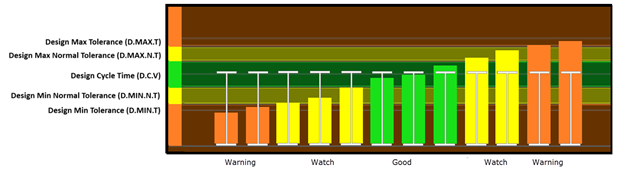
Tolerances
Overview
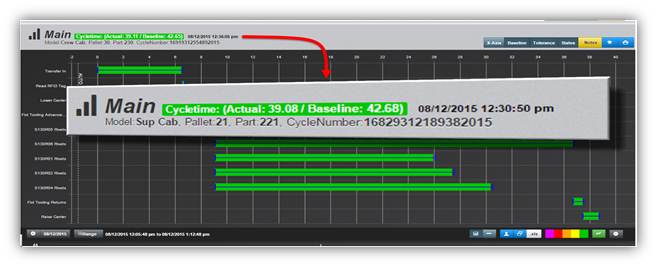
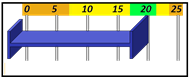
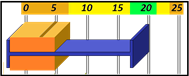
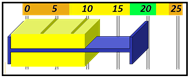
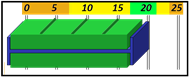
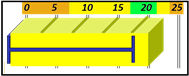
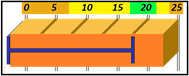
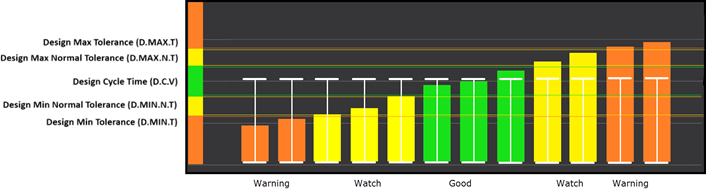
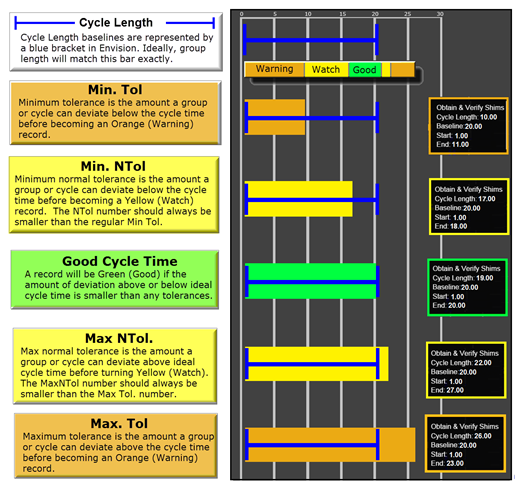
The Tolerances are preset in Envision to give a visual representation of the health of the cycle with a glance. In sequence, the base of the cycle is the Cycle Length. Cycle Length is represented by a Blue bracket on the graph. In a recorded cycle, it will show the length as compared to the Baseline tolerance. It will show a color based upon the performance of that cycle. Green for Good Cycle Length, Yellow to Watch, and Orange to give the operator a Warning. Below are the definitions of each in the Sequence and Heartbeat Views.
Cycle Length
Cycle Length baselines are represented by a |-- blue --|bracket in Envision. Ideally, group length will match this bar exactly.
Minimum Tolerance
Minimum Tolerance is the amount a group or cycle can deviate below the cycle time before becoming an Orange (Warning) record.
Minimum Normal Tolerance
Minimum Normal Tolerance is the amount a group or cycle can deviate below the cycle time before becoming a Yellow (Watch) record. The NTol number should always be smaller than the regular Minimum Tolerance (Min Tol).
Good Cycle Time
A Good Cycle Time record will be Green (Good) if the amount of deviation above or below ideal cycle time is smaller than any tolerances.
Maximum Normal Tolerance
Maximum Normal Tolerance (Max NTol) is the amount a group or cycle can deviate above ideal cycle time before turning Yellow (Watch). The MaxNTol number should always be smaller than the Maximum Tolerance (Max Tol) number.
Maximum Tolerance
Maximum Tolerance (Max Tol) is the amount a group or cycle can deviate above the cycle time before becoming an Orange (Warning) record.
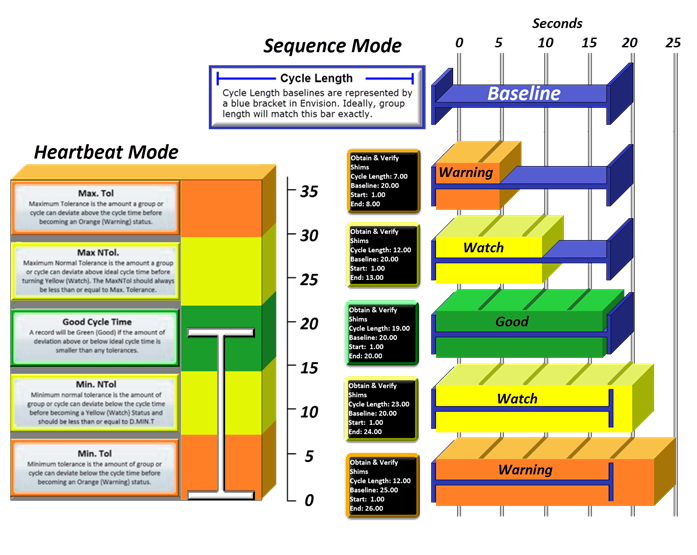
All in Heartbeat View
Tolerance Reference sheet
This example is shown in Sequence mode also shows the actual details if you hover the cursor over the cycle bar.
Tolerances in Heartbeat View